Sonora is a novel AI-powered system developed by Microsoft Research that enables real-time, voice-driven creation and navigation of immersive 3D audio environments. Designed to promote relaxation and reduce anxiety, Sonora blends cutting-edge AI technologies—including large language models (LLMs), audio diffusion models, and Unity3D game engine integration—to offer deeply personalized and interactive soundscapes.
Rethinking Soundscapes with AI
While traditional soundscapes offer passive relaxation, Sonora introduces a co-creative experience where users can speak naturally to an AI to add, remove, or reposition spatialized audio elements. Whether it’s the sound of ocean waves, birds overhead, or footsteps in snow, Sonora allows users to build calming environments in real time, tailoring the auditory world to their needs and preferences without relying on screens or visual interfaces.
System Architecture
Sonora features a modular architecture comprising:
- LLM modules (powered by GPT-4o) that interpret user input and manage sound generation and placement
- Audio diffusion models that synthesize realistic, non-pre-recorded sounds
- The “AI Conversationalist”, a voice-based interface offering guidance and emotional engagement
- A curated library of 482 diffusion-generated sounds for fast, high-quality experiences
The experience runs in Unity3D and can be accessed via VR or standard audio setups, allowing flexibility across environments and use cases.

Evaluating Impact: A User Study
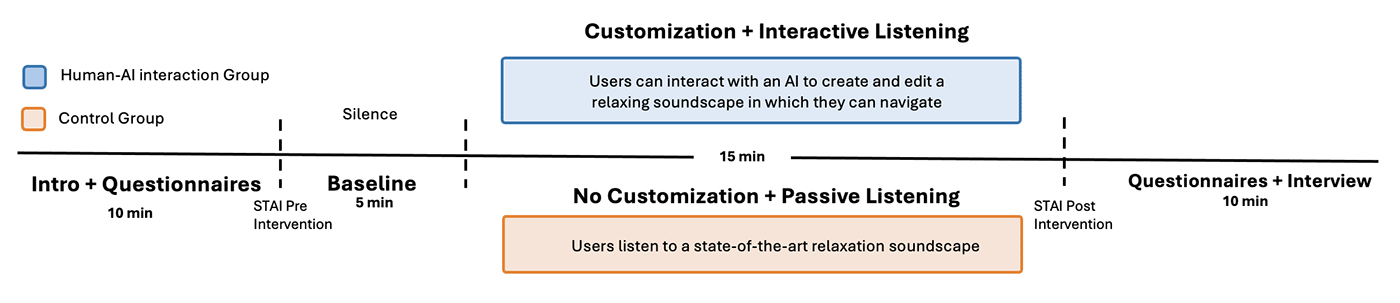
A controlled user study (n=32) compared Sonora to a state-of-the-art passive soundscape (Headspace). Key findings include:
- Participants rated Sonora as significantly more entertaining and engaging
- Users with moderate to high trait anxiety showed a significant reduction in state anxiety in both conditions, with Sonora offering greater interactivity
- No increase in cognitive load, despite the added complexity of interaction
- A positive correlation between anxiety levels and system engagement, suggesting Sonora is particularly appealing for anxious individuals

Anxiety was measured using the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). Participants were divided into two groups: moderate/high anxiety (STAI trait score ≥ 38) and low anxiety. A cutoff score of 38 is most commonly used to define clinically significant symptoms, which is considered when a patient no longer meets the diagnostic criteria for the disorder. For participants in the Sonora condition, those with moderate/high trait anxiety (13 per condition) showed a significant reduction in state anxiety (𝑝 < 0.001), while those with low anxiety showed no significant change (𝑝 = 0.570).
Real-World Implications
Sonora exemplifies the potential of AI-driven, screenless interaction paradigms to support mental health and well-being. By allowing users to «speak the world into existence» through voice commands, Sonora creates personalized, immersive 3D audio environments that can be used for stress relief, mindfulness practice, education, and immersive entertainment.
Future Applications
Beyond wellness, Sonora’s architecture opens doors to applications in gaming, accessibility, education, and therapeutic environments. The integration of fuzzy world modeling with spatial audio hints at new frontiers for naturalistic AI-human interaction in virtual environments.

